|
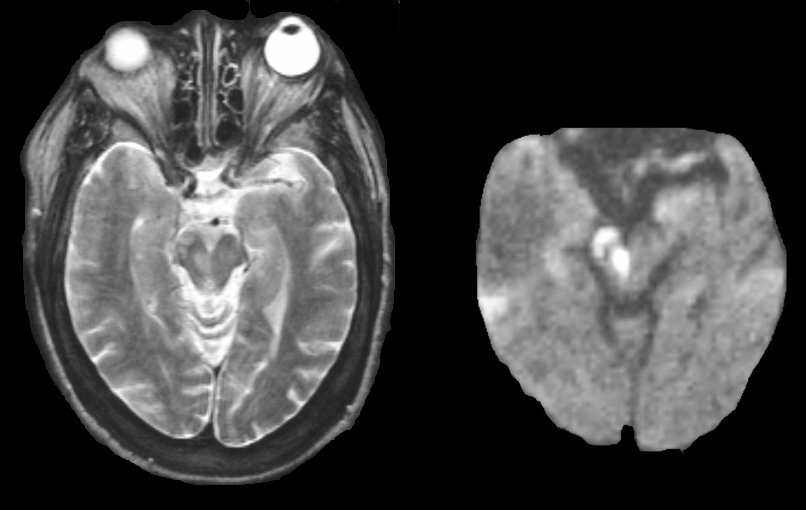
A 78 year-old woman developed the abrupt onset of a right third nerve palsy and a left hemiparesis. Sensation was intact. |

![]()
| Midbrain Infarction:
((Left) Flair axial MRI; (Right) Diffusion-weighted MRI. Note
the bright signal on the diffusion-weighted image in the ventral midbrain and cerebral
peduncle. Infarction in the midbrain results in a classic "crossed" neurology
syndrome of an ipsilateral 3rd nerve palsy and a contralateral hemiparesis,
known as Weber's syndrome. This infarct is in the distribution of one perforating branch of the basilar artery. This lesion is usually caused by the occlusion of one paramedian basilar branch, due to lipohyalinosis, which occurs as a result of aging, diabetes and hypertension. Occasionally these lesions are associated with intrinsic disease of the basilar artery or an embolus to the basilar artery. |
Revised
11/23/06
Copyrighted 2006. David C Preston